Recognized for Excellence
We're proud to share that our very own Dr. Ramin Fathi was named Top Doctors 2022, 2023, 2024, and 2025 by Phoenix Magazine, honoring his dedication to exceptional dermatologic care.
Phoenix's
Most Trusted
Skin Care Specialists
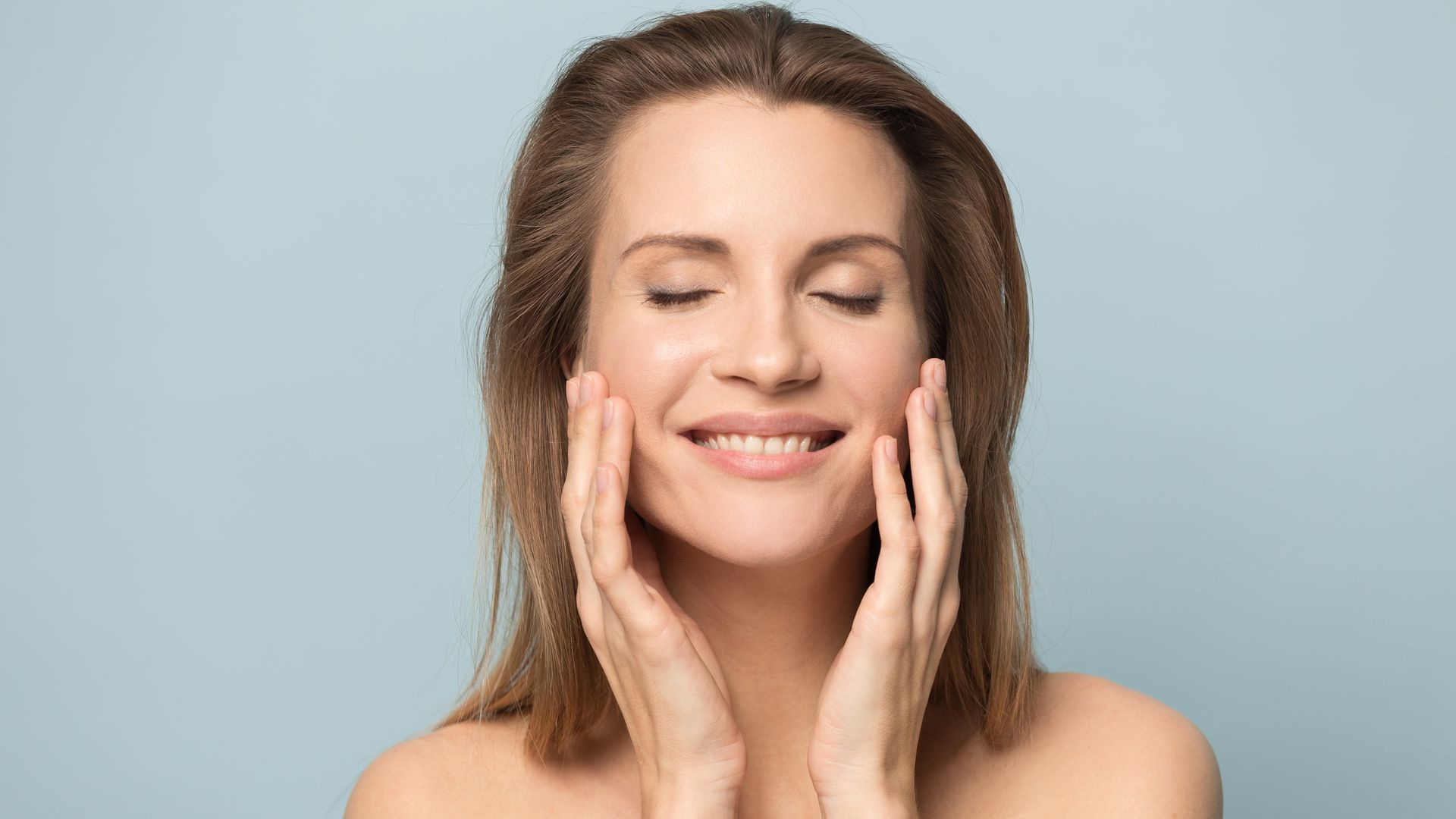
At Phoenix Surgical Dermatology Group, we deliver exceptional dermatologic care.
Our team of board-certified dermatologists is focused on patient comfort and clinic excellence.
Physician-Owned Practice
delivering personalized treatment plans
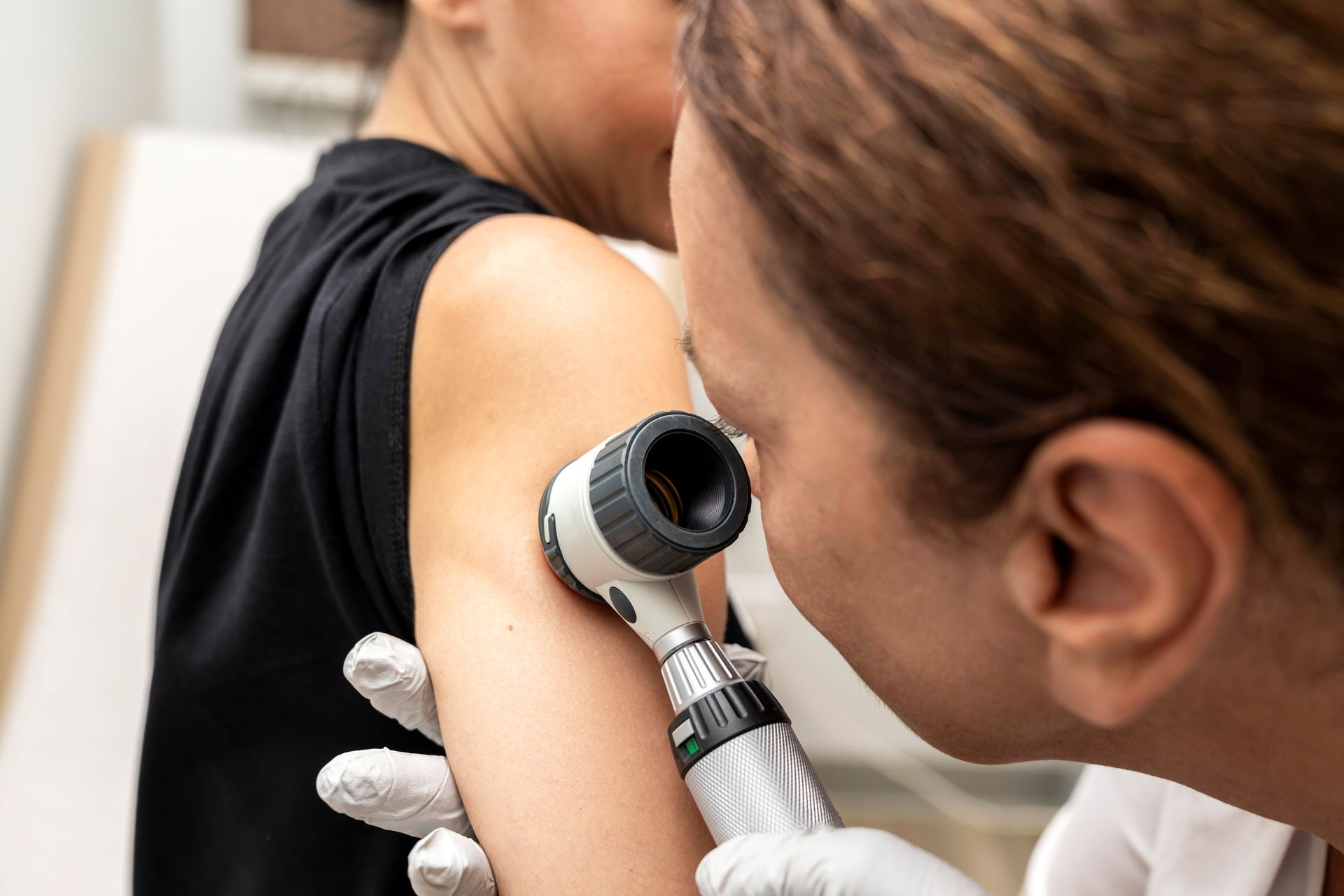
Advanced Skin Cancer Detection
with thorough examination techniques
Fellowship-Trained Mohs Surgeons
with high cure rates
Convenient North Phoenix Location
with plenty of easy-access, free parking
OUR SERVICES
Comprehensive Care from Expert Doctors
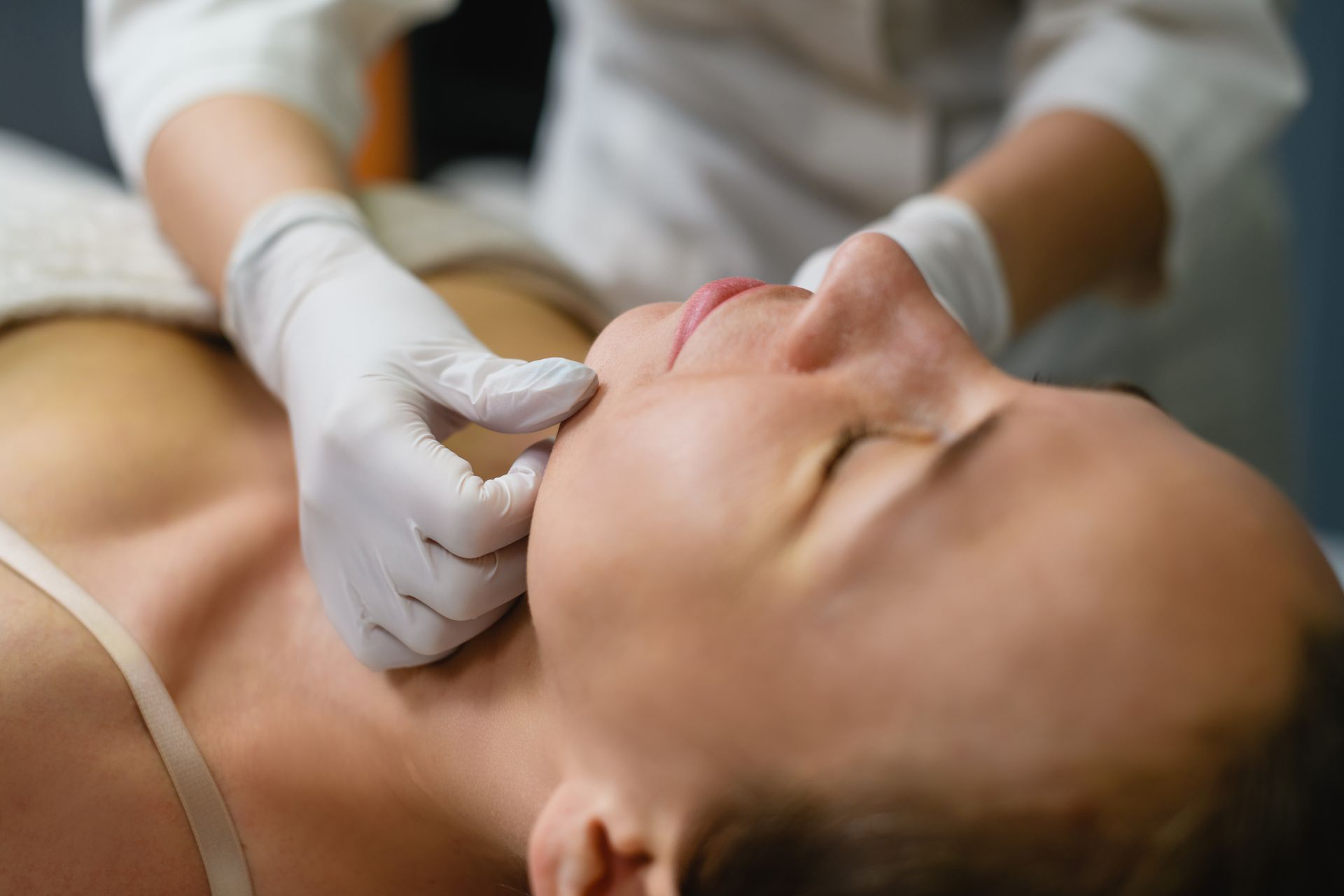
Medical Dermatology
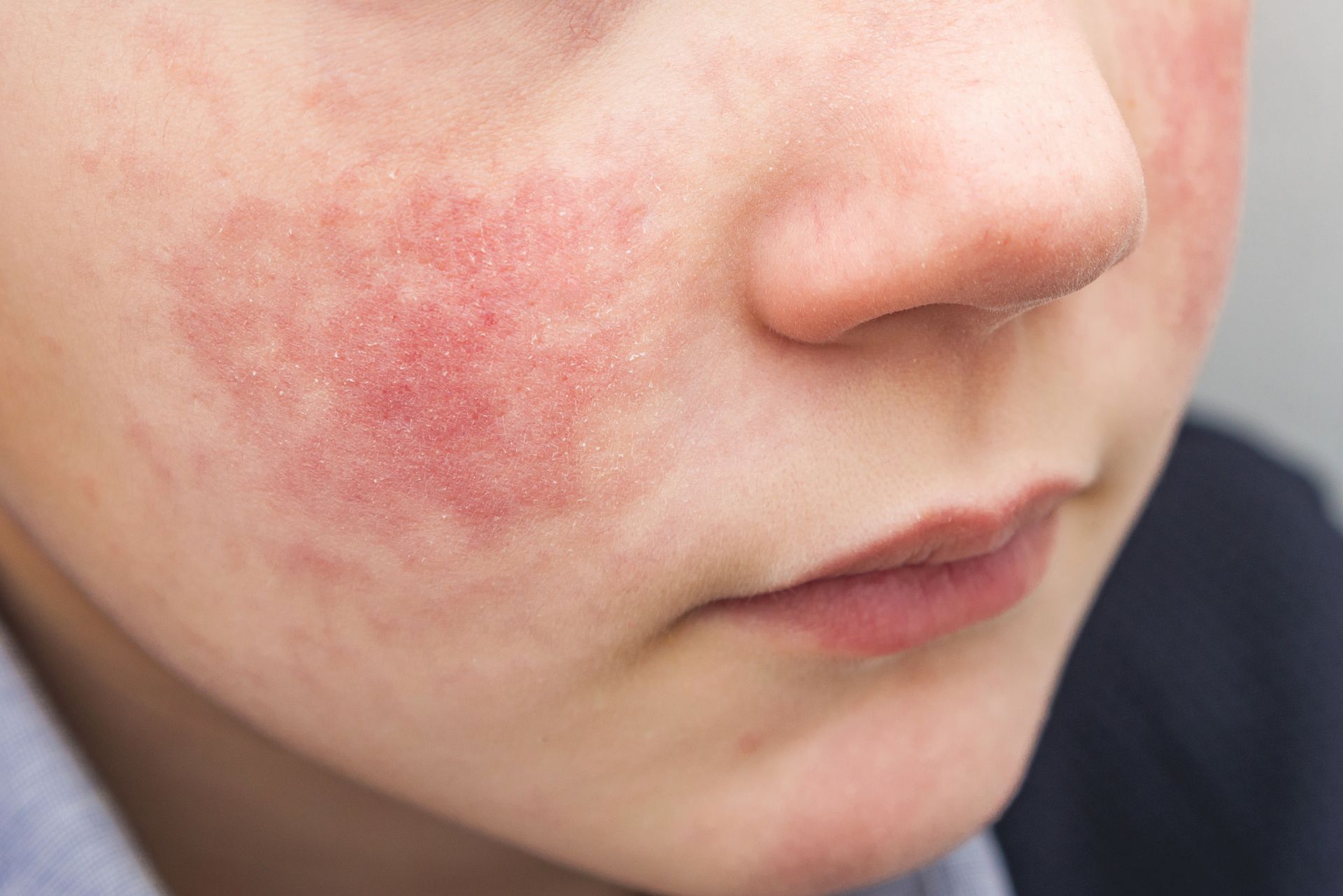
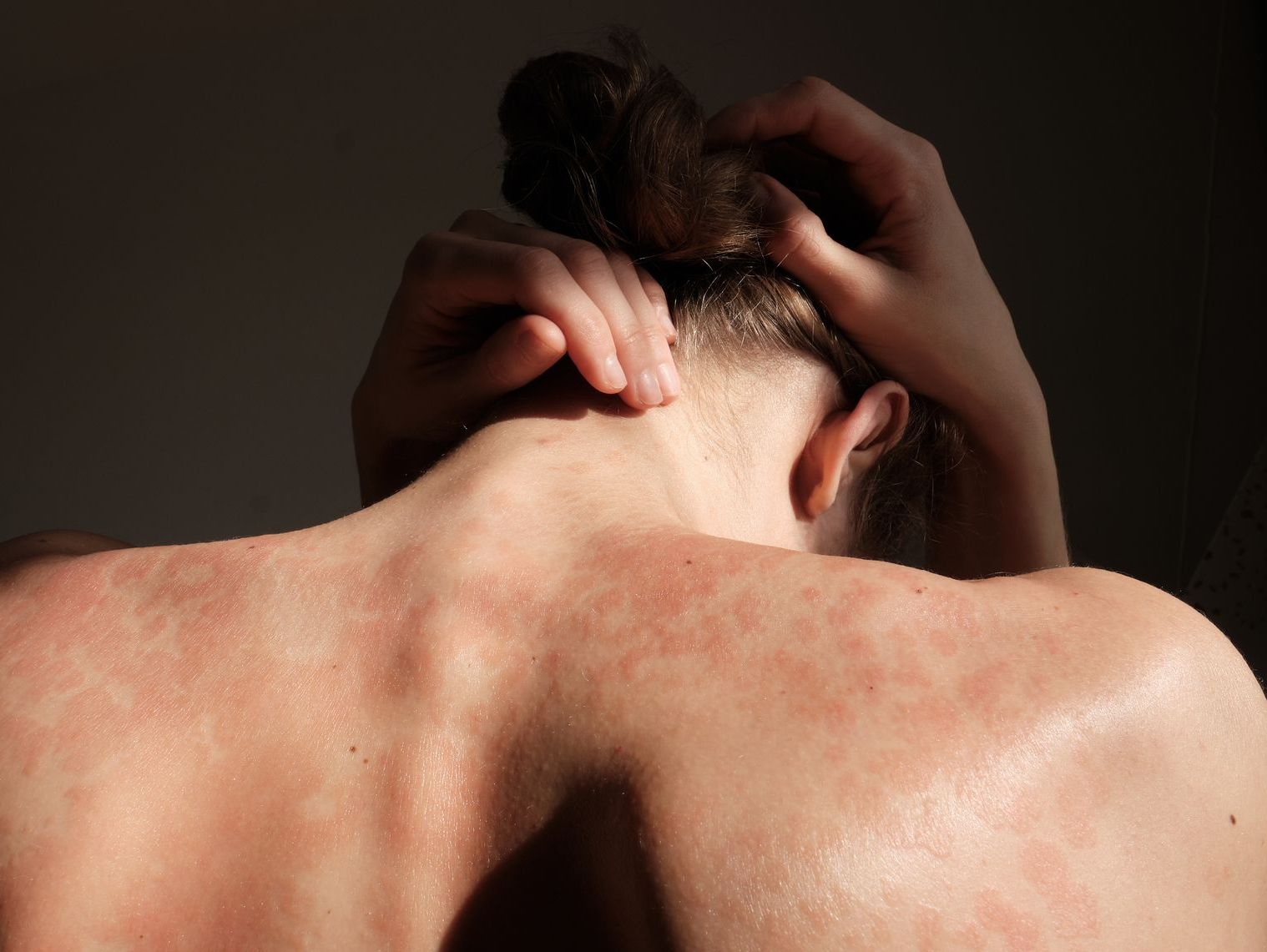
Our skin doctors provide expert diagnosis and treatment for acne, eczema, psoriasis, rosacea, and other skin conditions using the latest medical approaches.
Advanced Skin Cancer Care
Specialized Mohs surgery with 99% cure rates for skin cancer, performed by our fellowship-trained Mohs surgeons in our state-of-the-art facility.
Cosmetic Dermatology
Natural-looking enhancements through Botox, dermal fillers, laser skin rejuvenation, and personalized anti-aging treatments.
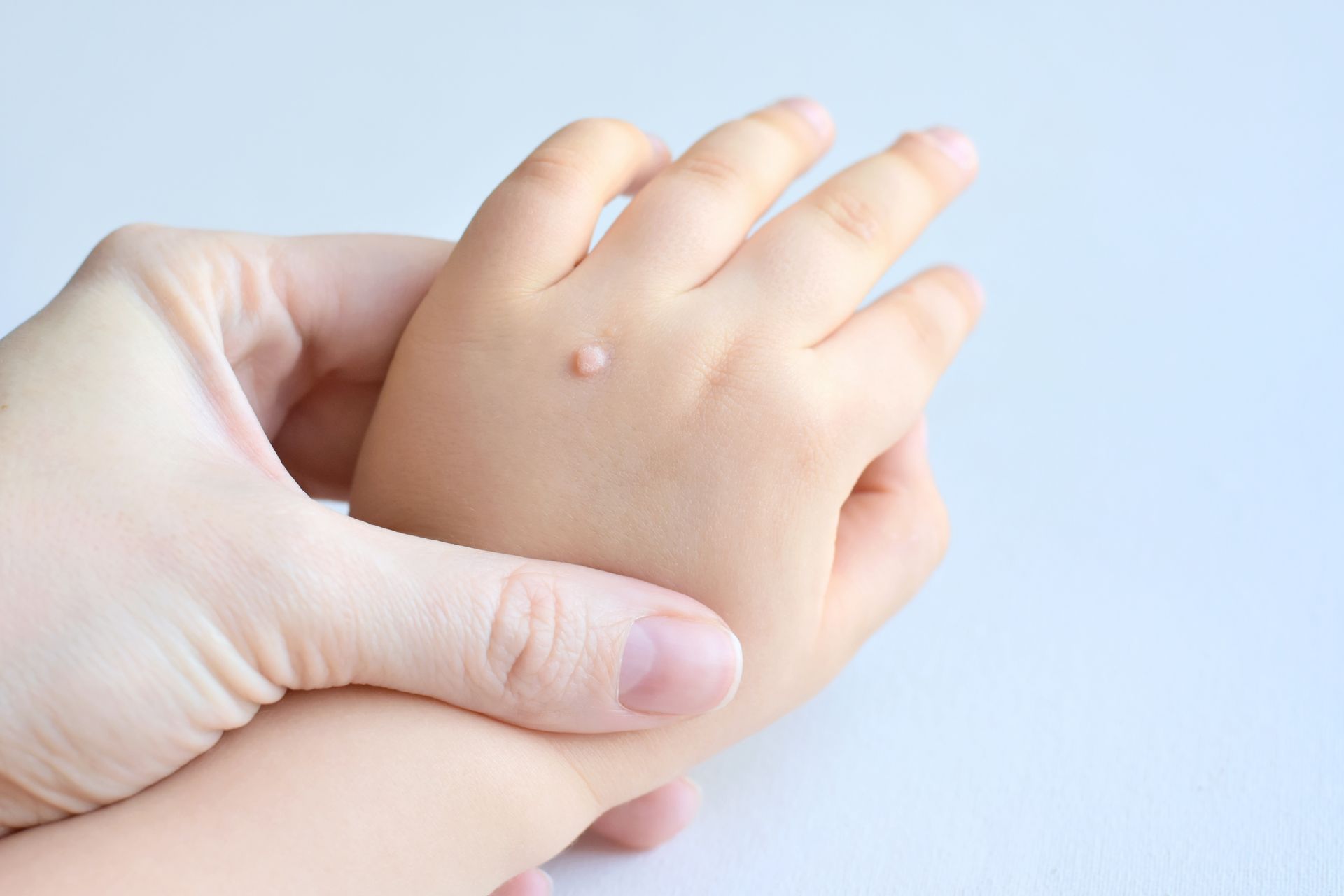
Pediatric Dermatology
Gentle, specialized care for children's skin conditions, including eczema, acne, birthmarks, and warts.
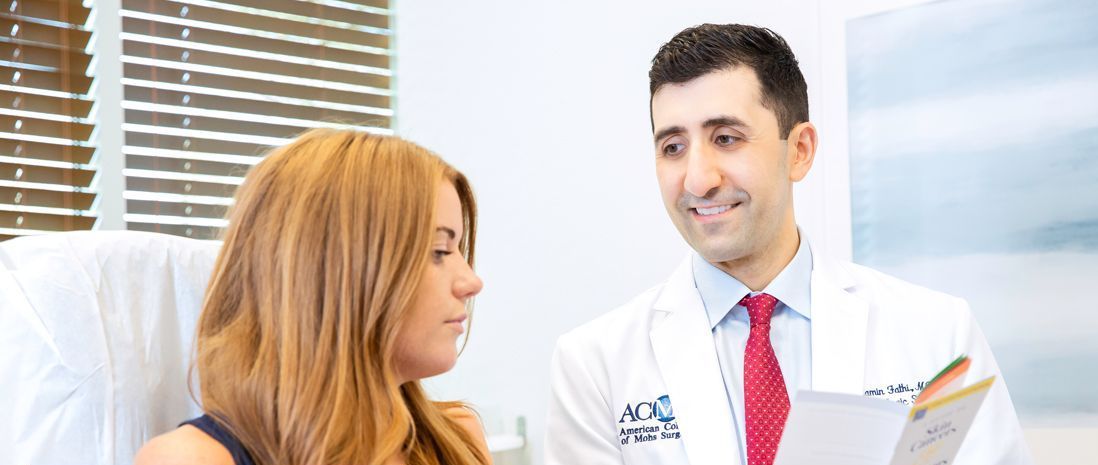
World-Class Expertise
Led by Dr. Ramin Fathi, our team of board-certified dermatologists and fellowship-trained Mohs surgeons is dedicated to the latest in skin care.
Patient-Centered Approach
We take time to listen, explain your options clearly, and create a care plan focused on your comfort and needs.
Community Commitment
Through our Shade the Kids program, we donate a portion of every visit to support sun safety and shade structures in Arizona schools.
Comprehensive Care
From skin checks to advanced surgery, we offer complete dermatologic care—all in one convenient location.
Join Us in Changing the Future of Arizona
For every patient we have the privilege to see, a part of our revenue directly contributes to building a shade structure at an elementary school in Arizona. It’s simple: when you take care of your skin with us, you’re also giving back. Helping yourself and the next generation.
CARE FOR EVERY SKIN TYPE + CONCERN
Expertise in a Wide Range of Skin Conditions
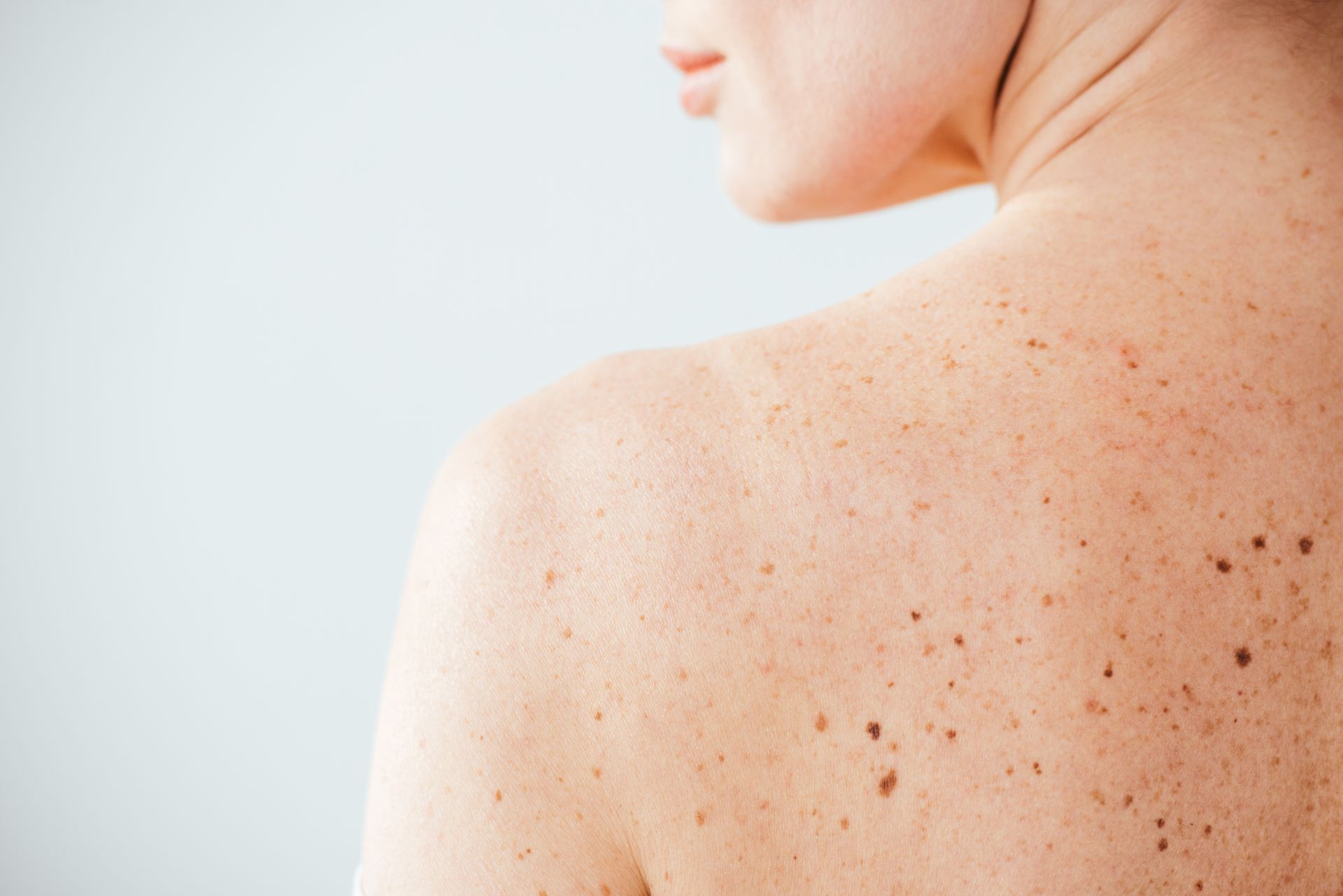
Skin Cancer
Detection and treatment of basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, melanoma, and precancerous lesions.
Common Skin Conditions
Specialized care for acne, eczema, psoriasis, rosacea, hair loss, excessive sweating, and allergic reactions.
Cosmetic Concerns
Solutions for wrinkles, volume loss, sun damage, acne scars, unwanted hair, and vascular lesions.
Skin Growths
Safe removal of moles, skin tags, warts, cysts, lipomas, and other benign growths.
TRUSTED BY PATIENTS LIKE YOU
Patient Testimonials
YOUR GUIDE TO GETTING STARTED
Patient Resources
Before Your Visit
Patient Convenience
FRESH FROM OUR FEED
@psdermgroup
FROM OUR EXPERTS TO YOU
Articles & Resources
LOOKING FOR "THE BEST DERMATOLOGIST NEAR ME" IN PHOENIX, ARIZONA?
Visit Us
4550 E Bell Road, Suite 150, Phoenix, AZ 85032
Hours
Monday — Friday
8 am — 4 pm